Break through in building
With our combined knowledge and our engineering capabilities, we are in one of the strongest positions to innovate new offerings and solutions to address key industry breakthroughs.
Mitek connectors:
how they work
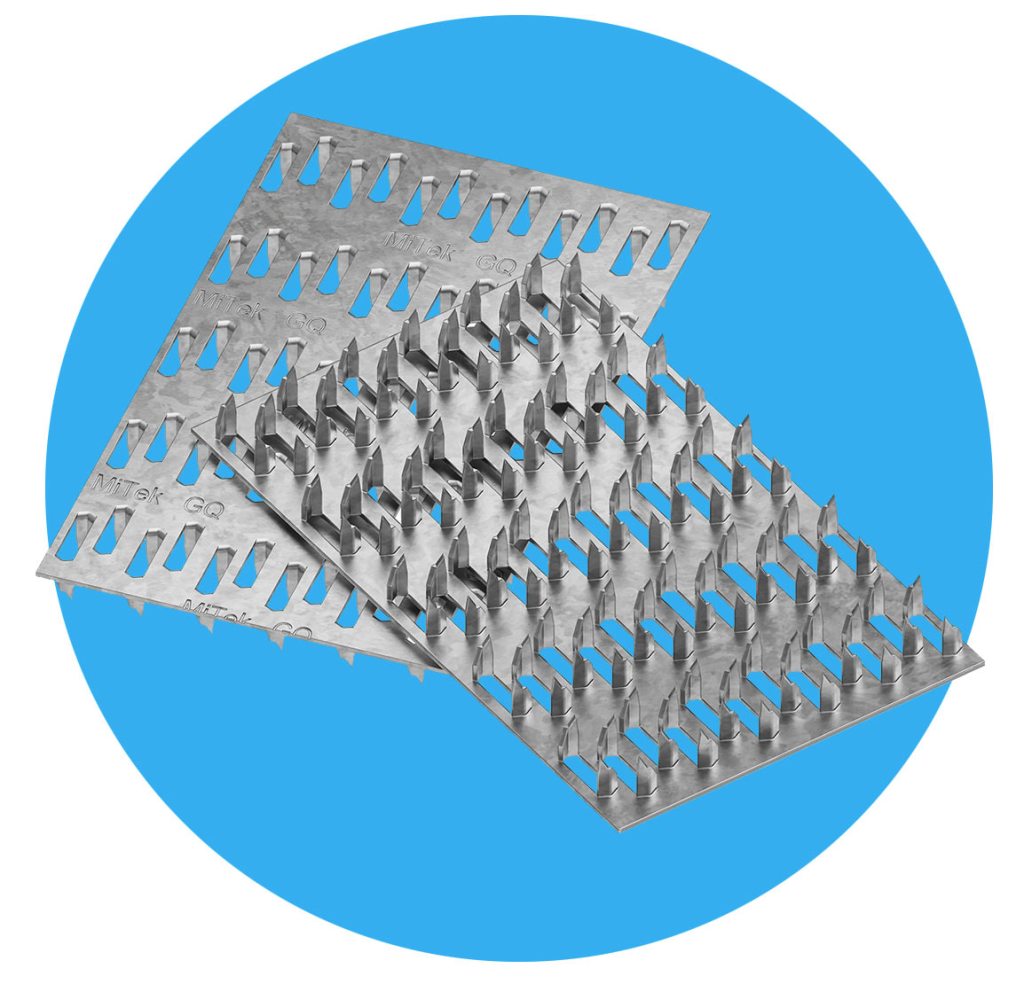
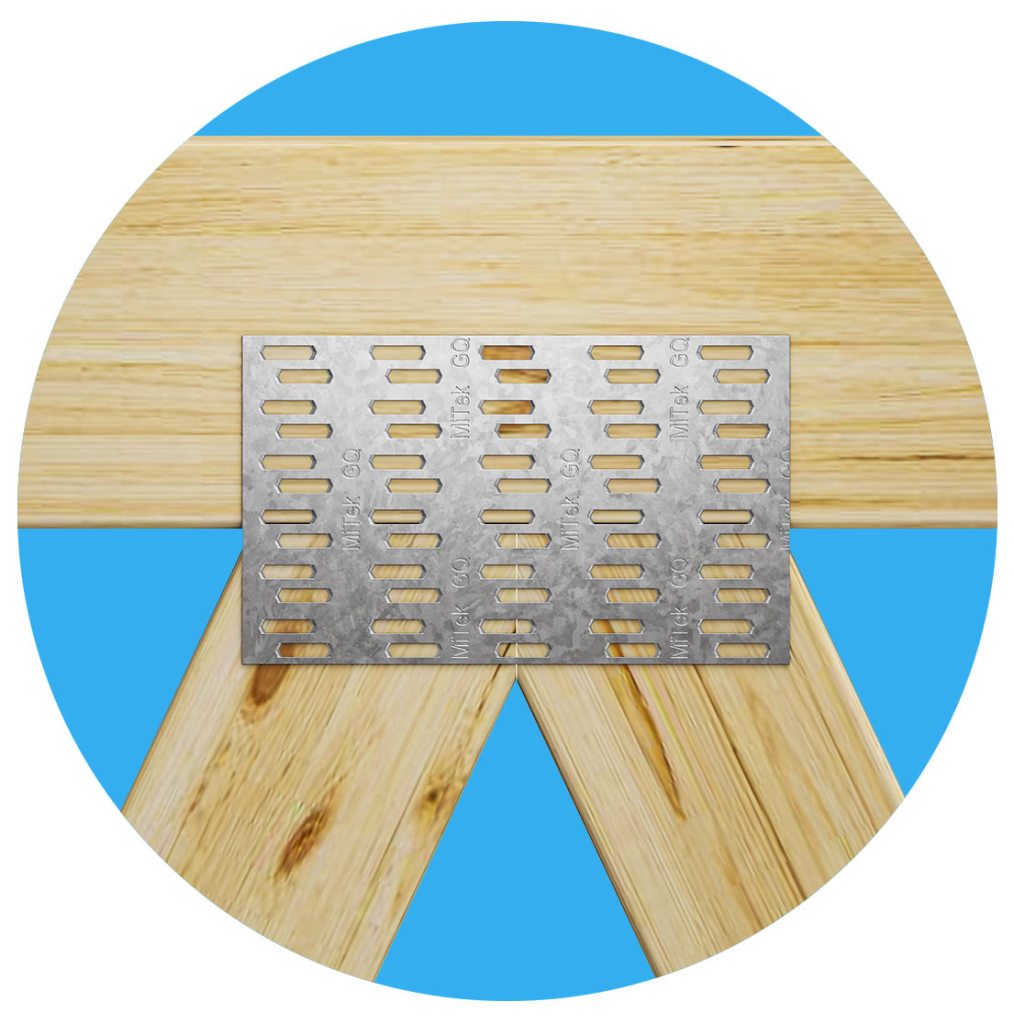
A MiTek connector plate is a steel plate with a collection of repeating spikes or nails projecting from one face. The spikes, (or teeth), are formed by punching slots in steel plates. These plates come in a number of different sizes. The teeth are then formed so they project at right angles to the plate. During this process the teeth are shaped to produce a rigid projection. When the teeth of a connector plate are pressed into timber laid end-to-end, the plate ‘welds’ them together by forming a MiTek joint. Connectors are always used in pairs with identical plates pressed into both faces of the joint.
The concept is simple but the design of efficient MiTek connectors requires careful balancing of tooth shape and density, connector plate thickness and ductility. An ongoing commitment to research and development ensures that MiTek’s licensed truss fabricators have the most efficient truss system at their disposal.
PERFORMANCE CRITERIA FOR MITEK CONNECTORS
| Plate Name | Steel Gauge | Steel Type | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| GQ | 20 gauge (Total Coated Thickness 1.0mm) | Steel Grade G300 Galvanised coating Z275 | General purpose connector. |
| GE | 18 gauge (Total Coated Thickness 1.2mm) | Steel Grade G300 Galvanised coating Z600 | For use when higher corrosive environment is required |
engineering data
MiTek connector plate properties have been established in accordance with designs based on Japanese building codes and standards. MiTek has obtained evaluation approvals from the Center of Better Living for GQ and GE MiTek Plate Connectors based on their structural evaluation system. MiTek’s software used to design trusses is evolving based on the needs of fabricators in Japan.
MiTek Australia Ltd. conducts regular tests on their existing connector range and monitors the long-term behavior of joints subjected to constant loading. Full-scale truss testing programs have also been carried out at the Universities of Western Australia and Adelaide, Australian National University, and the Cyclone Testing Station at the Capricornia Institute of Advanced Education in Cairns.
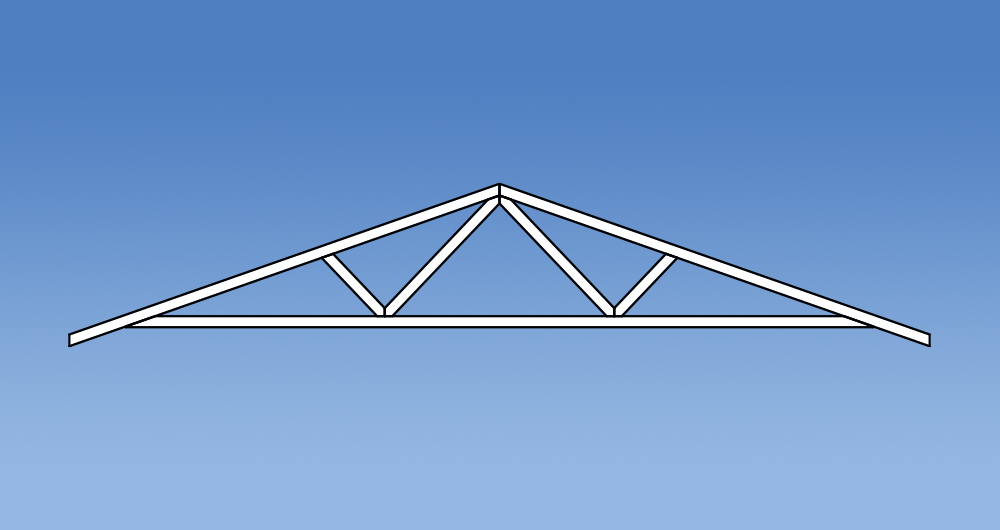
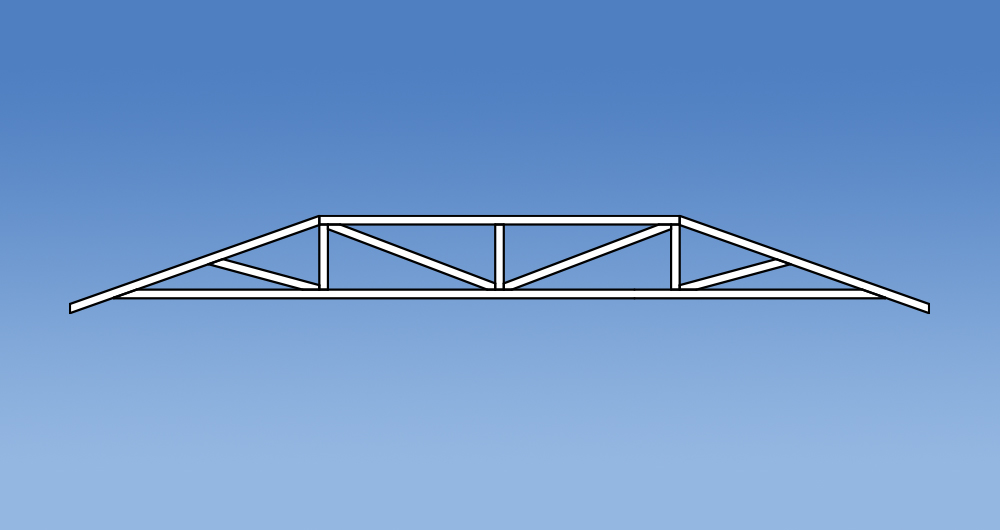
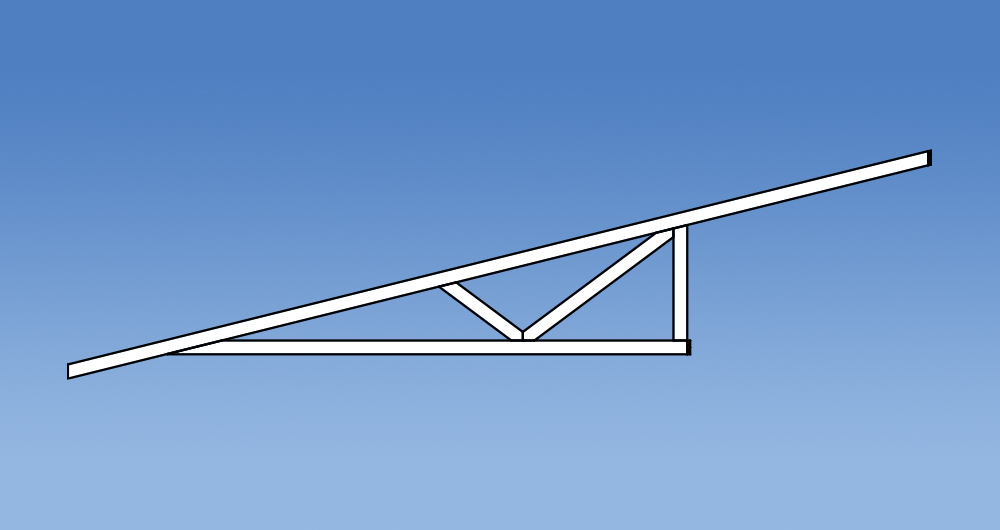
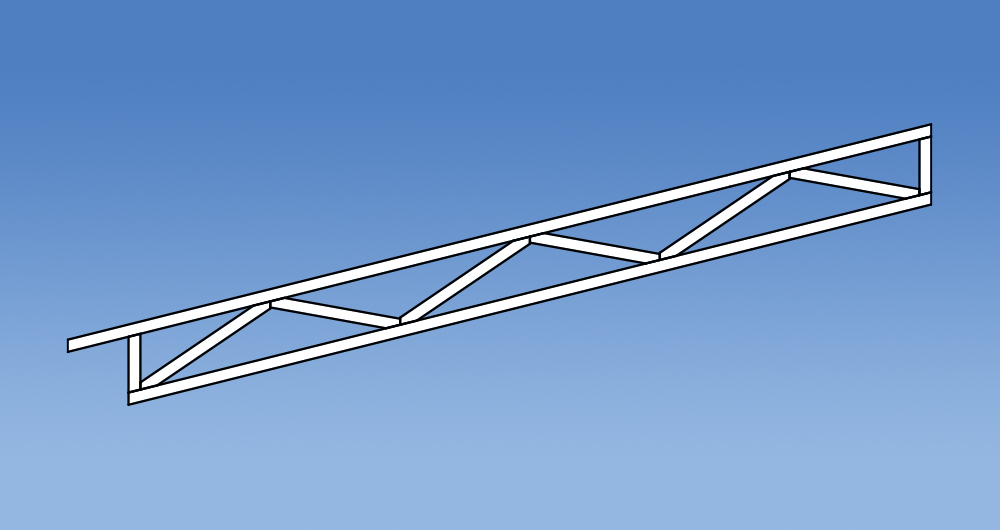
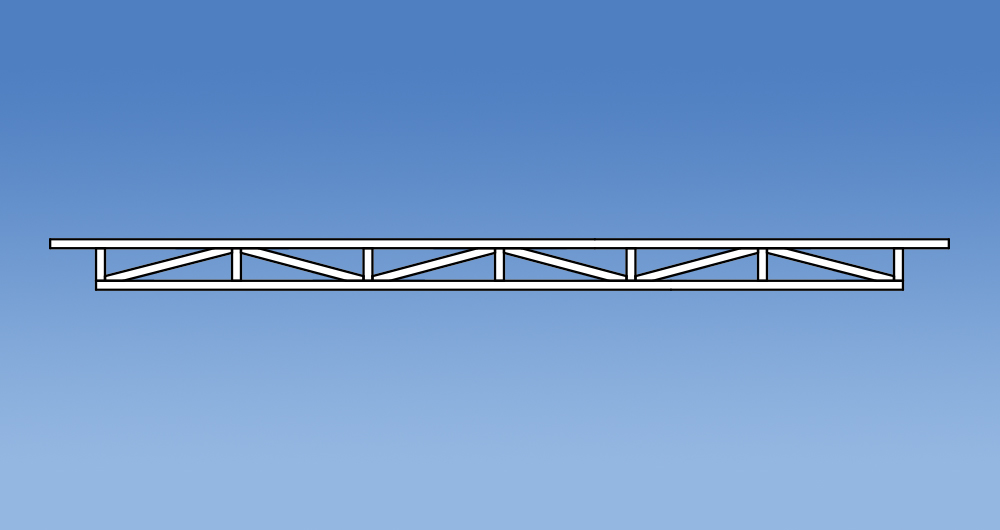
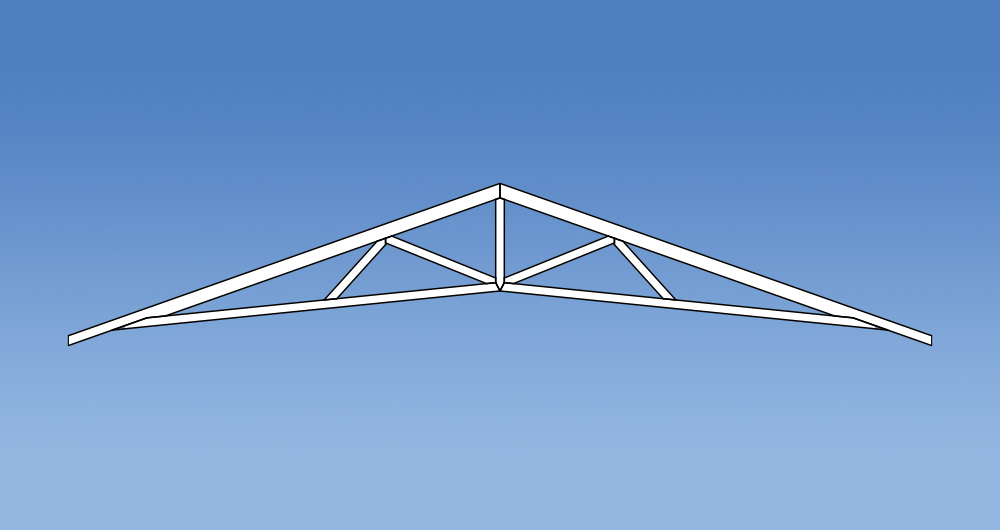
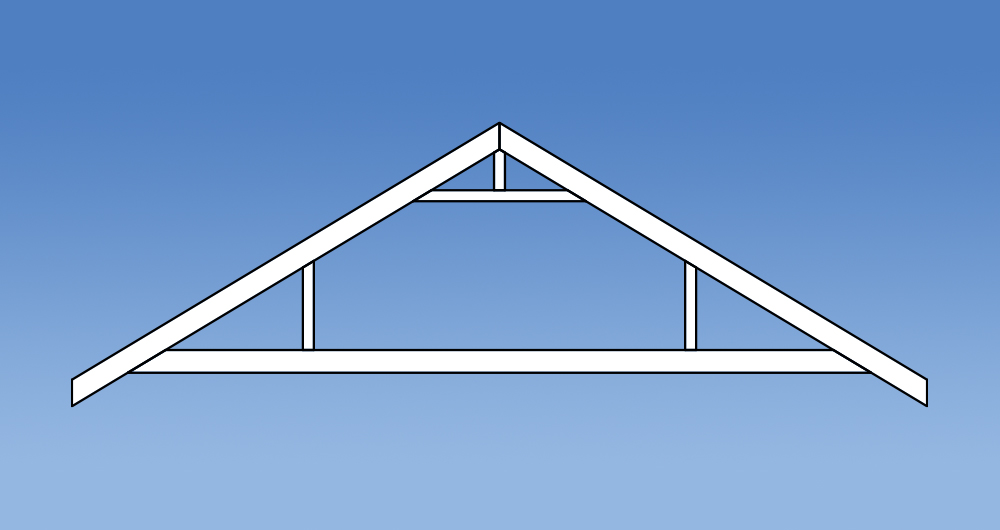
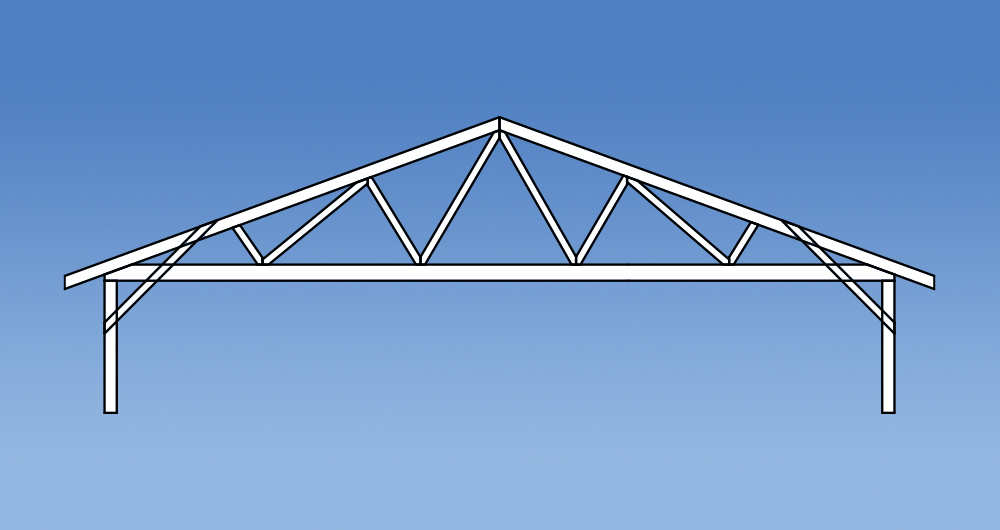
Versatility
Trusses have changed in design since the introduction of the Standard Truss. Prefabricated roof trusses now come in all shapes and sizes allowing them to accommodate voids, varying pitches and a multitude of roof layouts. Some commonly used truss configurations include: